As a software engineer, I think everyone can tell thousands of words about the differences between SQL vs NoSQL. And how to make a choice between them with your requirement.
Recently, I migrated the SaltyNote service from MariaDB to MongoDB. While the reason is not for high throughput or performance.
Be host, the important reason I changed to Mongo is that I need a more flexible schema for the note data.
If I stick to MariaDB, I need to have a separate table for note tags field for better aggregation and search later.
Info
I know some SQL database support JSON field, that can also be the solution. While instead of using JSON field, I prefer NoSQL.
For MariaDB
Without JSON field
1 | create table note ( |
Without JSON field, I need to create a separate table for note tags field, so I can query note by tags easily.
For example, to query all notes with tag java, I can use the following SQL:
1 | # Using * here is not a good practice, just for demo |
While this solution will bring some trouble when update tags, for example, if I have a note with tags java
and spring.
Later, I need to update the tags to java and spring-boot. I need to delete the old tags and insert the new tags. The
full update will include multiple actions.
1 | delete * from tag where note_id = 1; |
With JSON field
1 | create table note ( |
With JSON field, we can store the tags in the same table. And the update will be much easier, since we do not need to scan multiple rows.
1 | # query all notes with tag `java` |
On my research, I find Spring-Data-JPA does not support JSON field well. So I need to use native SQL to query and update, or introduce new dependency: Hibernate Types.
For MongoDB
For the reason above, eventually, I choose MongoDB. With MongoDB, I can store the tags in the same document with the note object.
Info
Transaction is not a concern for SaltyNote. Since it is OK to save duplicated notes, and user can simply delete it. (No duplicated notes have been found so far)
Pros:
- Flexible schema, so no need to do db migration when the schema changes.
- Great Spring boot integration, with Spring Data MongoDB, we can use the same repository interface as Spring Data JPA.
- Auto generated ID field works pretty well.
- All benefits of NoSQL.
Cons:
- Less knowledge than RDB, so it may take more time to set it up, and maintain it.
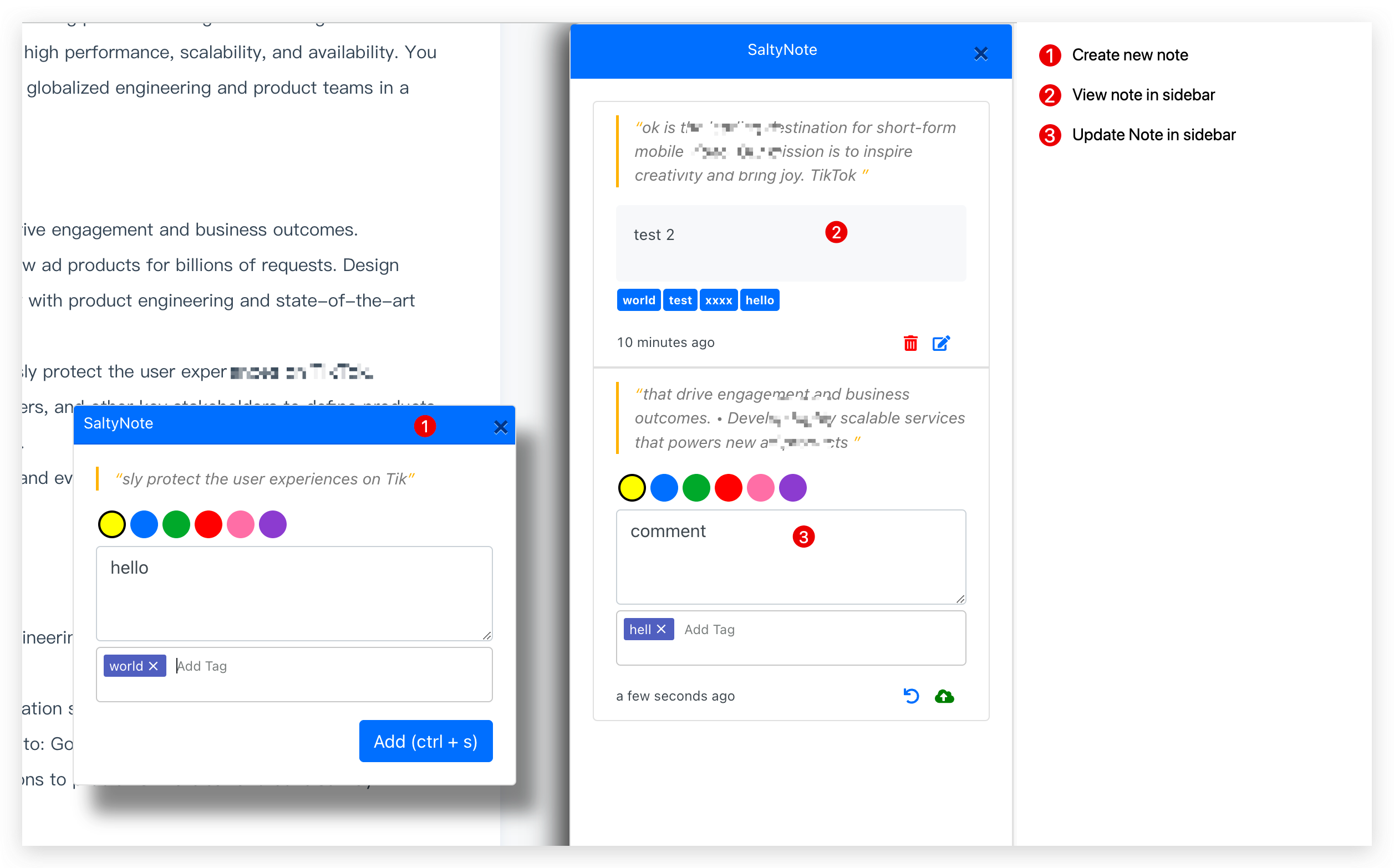
The Tag UI in Chrome Extension
The tag feature will be available in the next release of SaltyNote Chrome Extension v0.4.0.